Standardize and Compare Two Rates
Menu location: Analysis_Rates_Standardize and Compare Two Rates
This function calculates directly standardized rates (DSR) for two study populations, and then compares the DSRs as a rate ratio. Stratum-specific rates are compared also.
DSR is simply a weighted mean event rate for a study population, using the group/stratum sizes of a reference population as the weighting scheme. Standardized or adjusted rates are summary index measures for the purpose of comparison only; their magnitude has no intrinsic value.
The choice of a reference or standard population is important; it must relate to the population under study naturally.
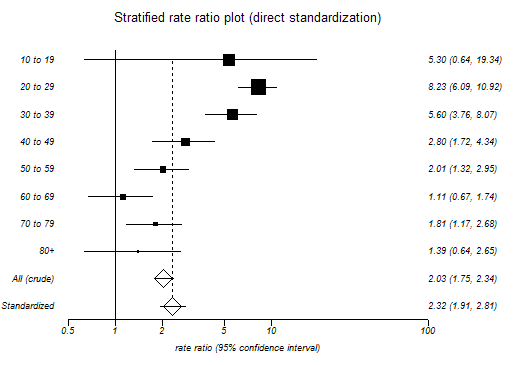
Please note that standardization is not a substitute for individual comparisons of stratum-specific rates. This function produces a plot of stratum-specific rate ratios in addition to comparing the standardized rates.
Direct standardization is not appropriate if there is not a consistent relationship between stratum-specific rates in different populations being compared. There are pitfalls in using directly standardized rates; if you have any doubts then please consult with an Epidemiologist and/or Statistician.
Some of the methods used here are unreliable with small numbers; generally, there should be at least 25 events observed overall and at least one event in each stratum. If the number of events is small, consider aggregating strata.
Note than an alternative binomial method is provided for situations where your observed rates are too large for the Poisson distribution to be used, namely one or more rates r are not so small that 1-r can be considered almost equal to 1.
See also:
Poisson rate confidence interval
- which provide some of the calculations given here either in more detail or with more options.
Data input
- Number of events for each group from index/study populations a and b
- Person-time for each group from index/study populations a and b (e.g. size of each group if just one year observed and all subjects followed up)
- Group sizes or weights from a reference/standard population
- Group/stratum labels, e.g. age bands
Technical validation
Exact Poisson confidence limits for the crude rates in both study populations are found as the Poisson means, for distributions with the observed number of events and probabilities relevant to the chosen confidence level, divided by time at risk. The relationship between the Poisson and chi-square distributions is employed here (Ulm, 1990):
- where Y is the observed number of events, Yl and Yu are lower and upper confidence limits for Y respectively, χ²ν, α is the chi-square quantile for upper tail probability α on ν degrees of freedom.
The two crude rates are compared as a ratio using Poisson distribution and test-based methods (Sahai and Kurshid, 1996):
- where IRD hat and IRR hat are point estimates of incidence rate difference and ratio respectively, m is the total number of events observed, PT is the total person-time observed and F is a quantile of the F distribution (denominator degrees of freedom are quoted last).
Approximate confidence intervals for the DSR are calculated firstly by Chiang's normal approximation to Poisson rate sums (Chiang, 1961; Keyfitz, 1966; Breslow and Day, 1987; Armitage and Berry, 1994) and secondly by an improved approximation adjusted for the total number of observed events (Dobson et al., 1991).
- where v is the approximate (Chiang) variance, wi is the reference weight for the ith stratum, ri is the observed study rate for the ith stratum, Ni is the reference population size for the ith stratum, yi is the number of events observed in the ith stratum of the study population, ni is the person-time for the ith stratum of the study population, z>α/2 is the (100 * α/2) the centile of the standard normal distribution, Y is the total number of events observed, Yl and Yu are the exact lower and upper confidence limits for the Poisson count Y and ICI l to u is the improved confidence interval due to Dobson et al. For large rates, the binomial variance is used, where r(1-r) is substituted for r in the variance formula above.
Approximate confidence intervals for standardized rate ratios are calculated as follows (Newman, 2001; Armitage et al., 2002):
- where SRR is the standardized rate ratio, var(log SRR) is the approximate variance of the natural logarithm of SRR, DSR and v are the directly standardized rate and its variance as above, zα/2 is the (100 * α/2) the centile of the standard normal distribution, and CI is the approximate confidence interval for SRR. For large rates, the binomial variance is used, where r(1-r) is substituted for r in the variance formulae above.
Example
From Newman (2001) p 254:
Test workbook (Rates worksheet: d1, pt2, d2, pt2, ref, age strata).
The following data relate to a retrospective cohort study of 2122 males who received treatment for schizophrenia in the province of Alberta, Canada during 1976-1985. The standard/reference population was taken as the Alberta general population in 1981.
| Age group | Deaths in Cohort | Person-Years in Cohort |
| 10-19 | 2 | 285.1 |
| 20-29 | 55 | 4,179.1 |
| 30-39 | 32 | 3,291.2 |
| 40-49 | 21 | 1,994.7 |
| 50-59 | 27 | 1,498.9 |
| 60-69 | 19 | 763.5 |
| 70-79 | 25 | 254.4 |
| 80 and over | 9 | 46.7 |
| Age group | Deaths in Alberta | People in Alberta (reference size) |
| 10-19 | 267 | 201,825 |
| 20-29 | 421 | 263,175 |
| 30-39 | 306 | 176,140 |
| 40-49 | 431 | 114,715 |
| 50-59 | 836 | 93,315 |
| 60-69 | 1,364 | 60,835 |
| 70-79 | 1,861 | 34,250 |
| 80 and over | 1,797 | 12,990 |
To analyse these data in StatsDirect you must select Standardize and Compare Two Rates from the rates section of the analysis menu. Note that annual mortality rates are often expressed as rates per 100000 population or units of person time (i.e. 100000 person years); .
For this example:
Comparison of two directly standardized rates
| Stratum | a | Person-time exposed | b | Person-time not exposed | Label |
| 1 | 2 | 285.1 | 267 | 201825 | 10 to 19 |
| 2 | 55 | 4179.1 | 421 | 263175 | 20 to 29 |
| 3 | 32 | 3291.2 | 306 | 176140 | 30 to 39 |
| 4 | 21 | 1994.7 | 431 | 114715 | 40 to 49 |
| 5 | 27 | 1498.9 | 836 | 93315 | 50 to 59 |
| 6 | 19 | 763.5 | 1364 | 60835 | 60 to 69 |
| 7 | 25 | 254.4 | 1861 | 34250 | 70 to 79 |
| 8 | 9 | 46.7 | 1797 | 12990 | 80+ |
| Stratum | RR | 95% CI (exact) | Weight | Label | |
| 1 | 5.302693 | 0.638882 | 19.343485 | 0.210839 | 10 to 19 |
| 2 | 8.227018 | 6.094736 | 10.916013 | 0.27493 | 20 to 29 |
| 3 | 5.596703 | 3.761033 | 8.069297 | 0.184007 | 30 to 39 |
| 4 | 2.802107 | 1.716758 | 4.338327 | 0.119839 | 40 to 49 |
| 5 | 2.010649 | 1.317034 | 2.946823 | 0.097483 | 50 to 59 |
| 6 | 1.1099 | 0.666146 | 1.740021 | 0.063552 | 60 to 69 |
| 7 | 1.808577 | 1.167342 | 2.678348 | 0.03578 | 70 to 79 |
| 8 | 1.393114 | 0.63598 | 2.650516 | 0.01357 | 80+ |
| All | 2.028063 | 1.746703 | 2.342474 | 1 | All (crude) |
Analysis model for rates: Poisson (small rates)
Rates are expressed per 1,000 units of person time:
Crude rate exposed = 15.430094
Exact 95% CI = 13.313979 to 17.786968
Crude rate not exposed = 7.608293
Exact 95% CI = 7.434549 to 7.785072
Standardized rate exposed = 17.616898
Approximate 95% CI = 14.217636 to 21.016159
Standardized rate not exposed = 7.608293
Approximate 95% CI = 7.433557 to 7.783028
Standardized rate ratio = 2.315486
Approximate 95% CI = 1.906565 to 2.812113